Your Complete Guide to Safe & Legal Child Travel, Including Booster Seat Age Florida Requirements
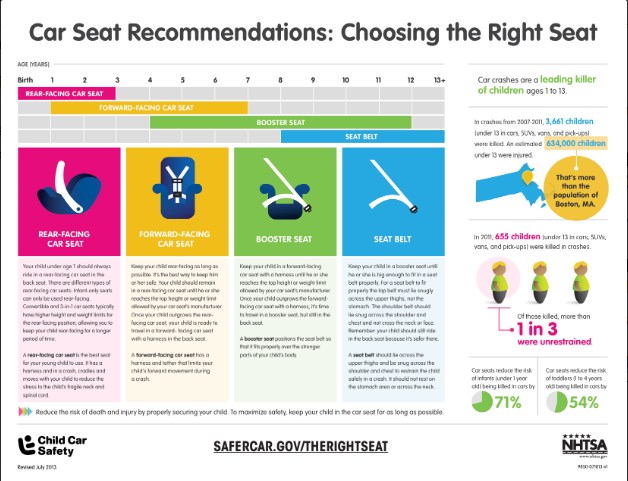
Ensuring the safety of child passengers is a top priority for parents and guardians. Car seat safety is crucial because it significantly reduces the risk of injury or death in the event of a car accident. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), properly used car seats can decrease the risk of fatal injury by 71% for infants and 54% for toddlers. Understanding specific regulations, such as booster seat age Florida requirements, highlights the importance of adhering to these guidelines to maximize safety. These statistics highlight the life-saving potential of correctly installed and used car seats, making them an indispensable part of child travel safety.
Florida has a strong commitment to child safety, reflected in its detailed car seat laws. These laws are designed to protect children of different ages, weights, and heights, ensuring they receive the appropriate level of protection while traveling in vehicles. By adhering to these regulations, parents and guardians can provide a safer travel environment for their children, significantly reducing the risk of injury in case of an accident.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to Florida’s car seat laws for 2024, ensuring that readers are well-informed about the latest regulations. Understanding these laws can sometimes be daunting due to the specific requirements based on a child’s age, weight, and height. However, this guide will break down these complexities, offering clear and concise information to help parents and guardians comply with the laws.
Readers will learn about the specifics of Florida car seat laws, including the different stages of car seats and the legal requirements for each. The article will also offer practical tips for the correct installation and use of car seats, ensuring maximum safety for child passengers. By the end of this guide, parents and guardians will have the knowledge and tools to keep their children safe and legally protected while traveling on Florida roads.
Overview of Florida Car Seat Laws
General Legal Framework
Florida’s car seat laws are established to ensure the safety of child passengers by mandating the use of appropriate child restraint systems based on a child’s age, weight, and height. These laws are designed not only to protect children but also to provide clear guidelines for parents and guardians, ensuring consistency in safety measures across the state.
Summary of Florida’s Car Seat Laws
The primary aim of Florida’s car seat laws is to minimize the risk of injury or death in the event of a car accident. The laws specify the type of car seat required for children of different ages and sizes, ensuring that each child receives the optimal level of protection. Key components of these laws include:
- Children under the age of 5 must be secured in a federally approved child restraint system.
- Infants and toddlers under the age of 3 must be in a separate car seat or the vehicle’s built-in child seat.
- Children aged 4-5 years can be in a separate car seat or a built-in child seat, depending on their size.
- Children aged 6-17 years must use a seat belt, but it is highly recommended that children remain in a booster seat until they are at least 4 feet 9 inches tall.
Legal Obligations for Drivers Transporting Children
Drivers are legally obligated to ensure that all child passengers are properly secured according to these laws. Failure to comply can result in fines and points on the driver’s license. Additionally, non-compliance poses significant safety risks to child passengers, who are more vulnerable in the event of a collision.
Current Legal Requirements (2024)
The 2024 Florida car seat laws continue to emphasize the importance of using age-appropriate child restraint systems. The laws are structured to provide detailed guidance based on the child’s developmental stage, offering maximum protection at each phase.
Overview of Car Seat Laws for Different Age Groups
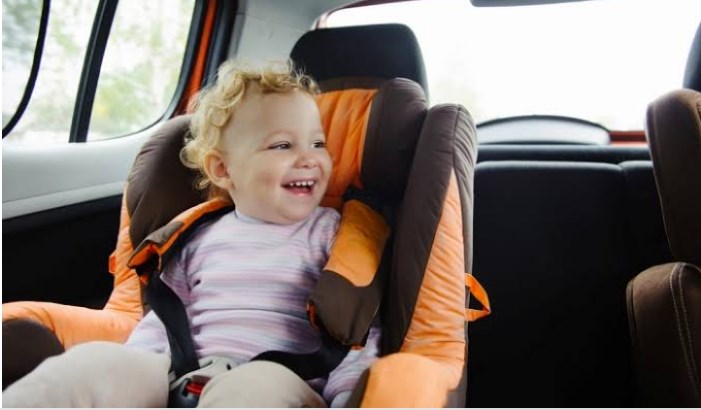
Infants (0-12 months): Infants must be secured in a rear-facing car seat. Rear-facing seats provide the best protection for the developing spine and neck in the event of a crash. Parents should ensure that the car seat is installed correctly and that the harness is adjusted to fit snugly.
Toddlers (1-3 years): Toddlers should remain in a rear-facing car seat until they reach the maximum height or weight limit specified by the car seat manufacturer. Once they outgrow the rear-facing seat, they can transition to a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether.
Preschoolers (4-5 years): Children in this age group should be secured in a forward-facing car seat with a harness until they exceed the seat’s height or weight limits. At this point, they can move to a booster seat, which positions the seat belt correctly over their body.
School-aged Children (6-12 years): Booster seats are recommended for children who have outgrown forward-facing car seats but are not yet tall enough for a seat belt to fit properly. A seat belt fits properly when the lap belt lies snugly across the upper thighs, not the stomach, and the shoulder belt rests across the chest, not the neck.
Teenagers (13-17 years): Once children are tall enough for the seat belt to fit correctly, they can use the vehicle’s seat belt system. The seat belt should fit without the need for a booster seat, ensuring that it provides adequate protection.
These requirements are designed to provide a graduated system of protection, adapting to the changing needs of growing children. By adhering to these laws, parents and guardians can ensure that their children are protected at every stage of development, reducing the risk of injury in the event of a car accident. The continuous review and adherence to these laws and guidelines are crucial for the safety and well-being of child passengers on Florida’s roads.
Legal Requirements for Child Restraint Systems
Children Aged 0-3 Years
Requirements for Rear-Facing Car Seats
For children aged 0-3 years, Florida law mandates the use of a rear-facing car seat. Rear-facing car seats provide the best protection for infants and toddlers because they support the head, neck, and spine in the event of a crash. These seats cradle the child, distributing the force of impact over the entire body, which is crucial for the delicate skeletal structure of young children.
Legal Specifications and Recommendations
- Rear-Facing Car Seat Requirement: Children must be secured in a rear-facing car seat until they reach the maximum height or weight limit specified by the car seat manufacturer. This typically includes children from birth until at least age two, though many experts recommend keeping children rear-facing for as long as possible, up to age three or beyond, if the car seat’s specifications allow.
- Installation Guidelines: The car seat must be installed in the back seat of the vehicle, never in the front seat, to avoid the danger posed by front airbags. The seat should be reclined at the proper angle to ensure the child’s airway remains open.
- Harness Adjustments: The harness should fit snugly, with the chest clip positioned at armpit level. The straps should be placed through the slots at or below the child’s shoulders.
Children Aged 4-5 Years
Options Between Separate Car Seats and Built-In Child Seats
For children aged 4-5 years, Florida law allows for more flexibility in choosing a restraint system. At this stage, children can transition from a rear-facing car seat to a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether. Some vehicles come equipped with built-in child seats that can also be used, provided they meet federal safety standards.
Transitioning Based on Size
- Forward-Facing Car Seat with Harness: Once a child outgrows their rear-facing car seat, they should be placed in a forward-facing car seat with a harness. This type of seat provides additional support for the child’s torso, neck, and head.
- Built-In Child Seats: Some vehicles have built-in child seats designed for children in this age group. These seats must meet all federal safety standards and should be used according to the vehicle manufacturer’s instructions.
- Harness and Tether Use: The forward-facing car seat should be installed in the back seat with a top tether and the vehicle’s seat belt or LATCH system. The harness should be adjusted so that it is snug, with the chest clip at armpit level and the straps at or above the child’s shoulders.
Children Aged 6-17 Years
Use of Seat Belts and Booster Seats
For children aged 6-17 years, Florida law requires the use of seat belts. However, it is recommended that children continue to use a booster seat until the seat belt fits them properly. This typically means that children should use a booster seat until they are about 4 feet 9 inches tall, which often corresponds to ages 8-12.
Recommended Practices for Booster Seat Use
- Booster Seat Usage: Booster seats are essential for positioning the seat belt correctly over a child’s body. The booster seat elevates the child so that the lap belt lies snugly across the upper thighs and the shoulder belt rests across the chest.
- Proper Seat Belt Fit: A proper seat belt fit occurs when the child can sit with their back against the vehicle seat, knees bent over the edge of the seat, and feet flat on the floor. The lap belt should lie flat across the upper thighs, not the stomach, and the shoulder belt should cross the center of the shoulder and chest, not the neck or face.
- Transition to Seat Belts Alone: Once a child is tall enough for the seat belt to fit correctly without a booster seat, they can use the vehicle’s seat belt system. Parents should regularly check the fit of the seat belt as the child grows to ensure it remains effective.
By adhering to these legal requirements and recommendations, parents and guardians can ensure that their children are provided with the highest level of protection while traveling in vehicles, significantly reducing the risk of injury in the event of an accident.
Age, Weight, and Height Considerations
Rear-Facing Car Seats
Guidelines and Best Practices
Rear-facing car seats are the safest option for infants and toddlers as they provide optimal support for the head, neck, and spine in the event of a collision. Best practices for using rear-facing car seats include:
- Use from Birth: Rear-facing car seats should be used from birth until the child outgrows the seat’s weight or height limits.
- Install in the Back Seat: Always install the rear-facing car seat in the back seat of the vehicle to avoid the dangers posed by front airbags.
- Recline Angle: Ensure the seat is installed at the correct recline angle, usually indicated on the car seat, to keep the child’s airway open.
- Harness Position: The harness straps should be at or below the child’s shoulders, fitting snugly with the chest clip at armpit level.
Recommendations Based on Manufacturer Limits
Each car seat comes with specific weight and height limits set by the manufacturer. It’s crucial to adhere to these limits to ensure safety:
- Check Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the car seat’s manual for the maximum weight and height limits.
- Extended Rear-Facing: Many modern car seats support extended rear-facing up to 40 pounds or more, allowing children to stay rear-facing beyond age two, which is recommended for increased safety.
Forward-Facing Car Seats
Transition Criteria and Safety Features
When a child outgrows their rear-facing car seat, they transition to a forward-facing car seat with a harness. The transition criteria typically include:
- Outgrowing Rear-Facing Limits: Transition to forward-facing once the child exceeds the rear-facing car seat’s weight or height limits.
- Harness and Tether: Use a forward-facing car seat with a harness and top tether, which provides additional support for the child’s head, neck, and torso in a crash.
Importance of Following Manufacturer Guidelines
To ensure maximum safety, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for forward-facing car seats:
- Harness Position: The harness straps should be at or above the child’s shoulders, fitting snugly.
- Installation: Secure the car seat in the back seat using the vehicle’s seat belt or LATCH system, and always use the top tether for added stability.
Booster Seats
Purpose and Usage of Booster Seats
Booster seats are designed to position the vehicle’s seat belt correctly on a child’s body, ensuring it fits properly:
- Purpose: Booster seats elevate the child so the seat belt fits across the upper thighs and chest rather than the stomach and neck.
- Usage: Children should use a booster seat until they are tall enough for the seat belt to fit correctly without it, usually around 4 feet 9 inches tall.
When to Transition to a Seat Belt
Transitioning from a booster seat to a seat belt should be based on the child’s height, not just age:
- Proper Fit: The seat belt should lie flat across the upper thighs and snugly across the chest and shoulder.
- Criteria: The child should be able to sit with their back against the vehicle seat, knees bent at the edge of the seat, and feet flat on the floor.
Seat Belts
Correct Fit and Usage
Using a seat belt correctly is crucial for ensuring safety once a child transitions out of a booster seat:
- Lap Belt Position: The lap belt should lie flat across the upper thighs, not the stomach.
- Shoulder Belt Position: The shoulder belt should cross the center of the shoulder and chest, avoiding the neck and face.
Criteria for Seat Belt Use
A child is ready to use a seat belt without a booster seat when they can:
- Sit Properly: Sit with their back against the vehicle seat, knees bent over the edge, and feet flat on the floor.
- Proper Belt Fit: The seat belt fits snugly across the upper thighs and chest, ensuring maximum protection.
Adhering to these age, weight, and height considerations for car seats and seat belts ensures that children are provided with the best possible protection while traveling, minimizing the risk of injury in the event of a crash.
Understanding Different Types of Car Seats
Rear-Facing Car Seats
Features and Benefits

Rear-facing car seats are designed to cradle and support infants and young toddlers, providing the best protection for their still-developing neck and spine. Key features include:
- Enhanced Safety: Rear-facing seats distribute the force of a crash over the entire body, significantly reducing the risk of injury.
- Supportive Design: They offer superior support for the head, neck, and spine, which is crucial for infants who have not yet developed strong neck muscles.
- Built-In Recline: Most rear-facing seats come with an adjustable recline to ensure the correct angle for airway maintenance and comfort.
Recommended Duration of Use
- Infancy to Toddlerhood: Rear-facing seats should be used from birth until at least age two, or until the child reaches the maximum weight or height limit set by the car seat manufacturer.
- Extended Rear-Facing: Many safety experts recommend keeping children rear-facing for as long as possible, up to the age of three or four, if the car seat’s specifications allow.
Forward-Facing Car Seats
Transition from Rear-Facing
Once a child outgrows their rear-facing car seat, they can transition to a forward-facing car seat. This transition typically occurs when the child exceeds the rear-facing seat’s height or weight limits.
Key Features and Usage Guidelines
- Harness System: Forward-facing car seats come with a five-point harness system that secures the child at the shoulders, hips, and between the legs, offering robust protection.
- Tether Strap: These seats often include a tether strap that anchors the top of the car seat to the vehicle, providing extra stability and reducing forward movement in a crash.
- Adjustable Headrests: Many forward-facing seats feature adjustable headrests to accommodate growing children and ensure a proper fit.
- Usage Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding weight and height limits, and ensure the harness is positioned at or above the child’s shoulders and fits snugly.
Booster Seats
Purpose and Correct Usage
Booster seats are designed to elevate children so that the vehicle’s seat belt fits properly. Their purpose is to ensure that the lap and shoulder belts are correctly positioned to provide effective restraint during a crash.
Guidelines for When to Switch to a Booster Seat
- Transition Criteria: Children should switch to a booster seat when they outgrow their forward-facing car seat, typically between the ages of 4 and 7, and once they meet the minimum weight and height requirements specified by the booster seat manufacturer.
- Proper Fit: The booster seat should raise the child so that the seat belt fits snugly across the upper thighs and chest, not the stomach or neck.
Seat Belts
Proper Seat Belt Use
Using the vehicle’s seat belt system is the final stage of child restraint. Proper seat belt use ensures that the child is adequately protected:
- Lap Belt Position: The lap belt should lie flat across the upper thighs, not the stomach, to prevent internal injuries in the event of a crash.
- Shoulder Belt Position: The shoulder belt should cross the center of the shoulder and chest, avoiding the neck and face to prevent choking and facial injuries.

When and How to Transition from a Booster Seat
- Transition Criteria: Children can transition from a booster seat to a seat belt when they reach approximately 4 feet 9 inches tall, typically between the ages of 8 and 12. They should be able to sit with their back against the vehicle seat, knees bent over the edge of the seat, and feet flat on the floor.
- Proper Fit Check: Ensure the seat belt fits correctly: the lap belt across the upper thighs and the shoulder belt across the chest. Regularly check the fit as the child grows to maintain safety.
By understanding the different types of car seats and their specific uses, parents and guardians can ensure that their children are provided with the best possible protection at each stage of their development. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions about car seat transitions and proper usage, enhancing child passenger safety on every journey.
Making the Transition
Criteria for Transitioning Car Seats
Factors to Consider: Age, Height, Weight
Transitioning a child from one car seat stage to another is a significant step that must be based on several critical factors to ensure their safety. The primary criteria for making these transitions include:
- Age: While age provides a general guideline, it should not be the sole factor. Different children develop at different rates, so it is essential to consider their physical development as well.
- Height: The height of the child is crucial for determining when to transition to a different car seat or to a booster seat. The child must fit properly within the height limits specified by the car seat manufacturer.
- Weight: Each car seat is designed to accommodate children within specific weight ranges. It is vital to adhere to these weight limits to ensure the car seat provides the necessary protection.
Safety Implications of Transitioning Too Early or Too Late
Transitioning a child to the next car seat stage either too early or too late can have serious safety implications:
- Transitioning Too Early: Moving a child to a forward-facing seat or a booster seat before they have outgrown their current seat can compromise their safety. Rear-facing seats provide better protection for the head, neck, and spine, especially in a frontal collision.
- Transitioning Too Late: Keeping a child in a car seat or booster seat beyond its height or weight limit can also be dangerous. The car seat may not provide adequate protection if the child exceeds its capacity, and an improperly fitting seat belt can cause injuries.

Manufacturer Guidelines
Importance of Adhering to Guidelines
Manufacturers provide specific guidelines for the use of their car seats, including weight and height limits, installation instructions, and proper usage tips. Adhering to these guidelines is crucial for ensuring the car seat functions as intended:
- Weight and Height Limits: Always follow the manufacturer’s specified weight and height limits for each stage of the car seat. These limits are based on rigorous testing and are designed to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the car seat.
- Installation Instructions: Proper installation is key to the car seat’s performance in a crash. Manufacturers provide detailed installation instructions, including whether to use the LATCH system or seat belt, and how to ensure the seat is secure and correctly positioned.
- Usage Tips: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines on harness positioning, recline angles for rear-facing seats, and the use of tethers for forward-facing seats. These tips help optimize the car seat’s protective capabilities.
Checking Fit and Adjustments
Regularly checking the fit of the car seat and making necessary adjustments is essential as your child grows:
- Harness Adjustments: Ensure the harness fits snugly and is positioned correctly at or below the child’s shoulders for rear-facing seats and at or above the shoulders for forward-facing seats. The chest clip should be at armpit level.
- Recline Angles: For rear-facing seats, regularly check the recline angle to ensure it remains appropriate as the child grows. Many car seats have adjustable bases or indicators to help maintain the correct angle.
- Headrest and Harness Slots: As the child grows, adjust the headrest and harness slots to the correct height. This ensures the car seat continues to provide optimal protection.
Transitioning a child from one car seat stage to another is a critical process that requires careful consideration of the child’s age, height, and weight. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines and regularly checking the fit and adjustments of the car seat are essential steps in maintaining the safety and protection of child passengers. By following these best practices, parents and guardians can ensure their children are safely secured during every journey.
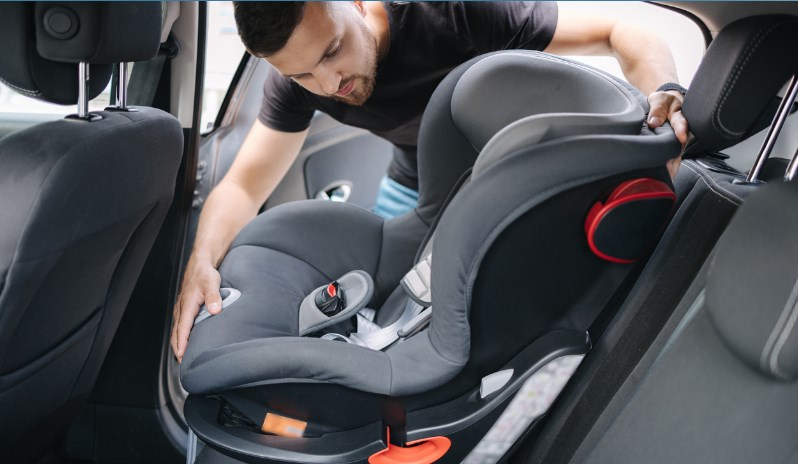
Installation and Usage Tips for Car Seats
Installation Tips
Reading and Understanding Manuals
One of the most critical steps in installing a car seat correctly is thoroughly reading and understanding the manuals. This includes both the car seat manual and the vehicle owner’s manual. These manuals provide specific instructions on:
- Compatibility: Understanding the compatibility between the car seat and the vehicle ensures that the seat can be installed securely.
- Installation Methods: Detailed steps for installation, which vary depending on the type of car seat and the vehicle.
Using LATCH System vs. Seat Belt
Most cars manufactured after 2002 are equipped with the LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) system, which simplifies the installation of car seats.
- LATCH System:
- Lower Anchors: Connect the car seat’s lower attachments to the vehicle’s lower anchors.
- Tether Anchor: Use the top tether anchor for additional security, especially with forward-facing seats.
- Tightness: Ensure that the seat does not move more than an inch from side to side or front to back.
- Seat Belt Installation:
- Threading the Belt: Thread the seat belt through the designated path on the car seat and buckle it.
- Locking the Seat Belt: Use the seat belt’s locking mechanism to secure the car seat.
- Tightness: Check the tightness to ensure minimal movement.
Ensuring Tightness and Proper Angle
Proper tightness and angle are essential for the car seat’s effectiveness.
- Checking Tightness: After installation, the car seat should not move more than one inch in any direction.
- Correct Angle: Ensure rear-facing seats are reclined at the correct angle to keep the child’s airway open. Many car seats have angle indicators to assist with this.
Usage Tips
Correct Harness Positioning
Proper harness positioning is vital for the child’s safety.
- Harness Height: For rear-facing seats, the harness should be at or below the child’s shoulders. For forward-facing seats, the harness should be at or above the shoulders.
- Snug Fit: The harness should be snug enough that you cannot pinch any excess webbing at the child’s shoulder.
- Chest Clip: Position the chest clip at armpit level to ensure it performs effectively in a crash.
Avoiding Bulky Clothing
Bulky clothing can interfere with the harness’s fit.
- Thin Layers: Dress the child in thin layers and use blankets over the harness if needed.
- Harness Adjustment: Adjust the harness snugly over thinner clothing for a secure fit.
Regular Adjustments
As the child grows, regular adjustments are necessary to maintain a proper fit.
- Harness Slots: Move the harness to higher slots as the child grows.
- Headrest: Adjust the headrest to ensure it provides adequate support.
- Routine Checks: Regularly check the fit and adjust the harness and car seat as needed.
Car Seat Maintenance and Replacement
Inspecting for Wear and Tear
Regular inspection of the car seat ensures it remains in good condition.
- Check Components: Inspect straps, buckles, and plastic parts for wear and tear.
- Cleaning: Follow the manufacturer’s cleaning instructions to maintain the seat’s integrity.
Following Expiration Dates
Car seats have expiration dates due to material degradation and evolving safety standards.
- Locate the Expiration Date: Find the expiration date on the car seat label or in the manual.
- Adherence: Replace the car seat once it reaches its expiration date to ensure continued safety.
Replacing Car Seats After Accidents
Car seats must be replaced after moderate to severe accidents to ensure they continue to provide adequate protection.
- Inspection: Even if no damage is visible, the car seat’s structural integrity could be compromised.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the car seat manufacturer’s recommendations regarding replacement after an accident.
Proper installation and usage of car seats are critical for ensuring child passenger safety. By thoroughly understanding installation methods, maintaining correct usage practices, and adhering to maintenance and replacement guidelines, parents and guardians can significantly enhance their children’s safety on the road.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Placement Errors
Correct Placement Within the Vehicle
One of the most common mistakes parents and guardians make is placing the car seat in an incorrect position within the vehicle. The safest place for a child in a car seat is typically in the back seat, away from active airbags that can cause severe injury in a crash.
- Rear Middle Seat: The center of the rear seat is often the safest spot because it is farthest from any impact during a collision.
- Avoid Front Seats: Never place a rear-facing car seat in the front seat if there is an active airbag. Even with forward-facing seats, the back seat is generally safer.
Incorrect Harness Positioning
Ensuring the Harness is Snug and Correctly Positioned
Proper harness positioning is crucial for the safety and effectiveness of the car seat. Incorrectly positioned or loose harnesses can significantly reduce the car seat’s ability to protect the child.
- Harness Height: For rear-facing seats, the harness straps should be positioned at or below the child’s shoulders. For forward-facing seats, the straps should be at or above the shoulders.
- Snug Fit: The harness should be tight enough that you cannot pinch any excess webbing at the child’s shoulders. A snug harness ensures that the child is securely held in place.
- Chest Clip: The chest clip should be positioned at armpit level to keep the harness straps in the correct position over the child’s shoulders.
Wrong Seat for Child’s Size
Avoiding Premature Transitions
Transitioning a child to the next car seat stage too early is a common mistake that can jeopardize their safety. Each car seat stage is designed to provide optimal protection for specific age, weight, and height ranges.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the weight and height limits specified by the car seat manufacturer. Do not transition to the next stage until the child exceeds these limits.
- Extended Use: Keep children in each car seat stage for as long as possible within the recommended limits. Rear-facing seats, for example, offer the best protection for young children and should be used until the maximum height or weight limit is reached.
Improper Securing
Checking for Movement and Tightness
A car seat that is not securely installed can move excessively, reducing its effectiveness in a crash.
- Installation Tightness: After installing the car seat, check that it does not move more than one inch side to side or front to back. Use the vehicle’s seat belt or LATCH system to secure the seat tightly.
- Regular Checks: Routinely check the tightness of the installation, especially if the car seat is frequently moved between vehicles.
Forgetting Registration
Importance of Registering Car Seats
Registering your car seat with the manufacturer is a simple but often overlooked step that can be crucial for safety.
- Receive Recalls and Safety Notices: Registration ensures that you receive important updates about recalls or safety notices directly from the manufacturer.
- Easy Replacement: In the event of a recall, registered owners are typically given priority for replacements or repairs.
Ignoring Expiration Dates
Risks of Using Expired Car Seats
Car seats have expiration dates for a reason. Over time, the materials in the car seat can degrade, and safety standards may change.
- Expiration Date: Always check the car seat’s expiration date, which is usually found on a label on the seat or in the manual.
- Replace as Needed: Replace the car seat once it reaches its expiration date to ensure it continues to provide the intended level of protection.
Avoiding these common mistakes is essential for maintaining the safety of child passengers. Proper placement, harness positioning, appropriate seat selection, secure installation, timely registration, and adherence to expiration dates all contribute to the effective use of car seats. By being vigilant and informed, parents and guardians can significantly enhance the safety of their children while traveling.
Resources for Florida Parents
Car Seat Inspection Stations
Locations and Services Provided by Florida Highway Patrol and Safe Kids Coalitions
Ensuring that a car seat is installed correctly can be challenging, but numerous resources are available to help parents and guardians in Florida. Car seat inspection stations provide an invaluable service by having certified child passenger safety technicians check the installation and usage of car seats.
- Florida Highway Patrol (FHP): Many FHP stations offer free car seat inspections. Trained technicians can assist with installing car seats correctly and provide educational resources to ensure ongoing compliance with safety standards.
- Safe Kids Coalitions: Safe Kids Coalitions across Florida frequently hold car seat inspection events. These coalitions focus on preventing childhood injuries and offer hands-on help with car seat installation and adjustments. You can find local inspection events and resources by visiting the Safe Kids website and locating your nearest coalition.
Online Resources and Guides
Websites for Florida Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles (FLHSMV)
The Florida Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles (FLHSMV) provides comprehensive information on car seat laws and safety tips on its website. Key resources include:
- Car Seat Laws and Regulations: Detailed explanations of Florida’s car seat laws, including age, weight, and height requirements for various stages.
- Safety Tips: Practical advice on choosing, installing, and using car seats properly to ensure maximum safety for child passengers.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Resources
The NHTSA website is another excellent resource for car seat safety information. It offers a variety of tools and guides, such as:
- Car Seat Recommendations: Guidelines for choosing the right car seat based on a child’s age, height, and weight.
- Installation Videos: Step-by-step video tutorials for installing different types of car seats.
- Inspection Station Locator: A tool to help parents find nearby car seat inspection stations.
Community Programs and Workshops
Local Hospitals, Fire Departments, and Community Centers Offering Car Seat Safety Programs
Many local organizations offer car seat safety programs to help parents and guardians ensure their children are properly secured. These programs often include:
- Hospitals: Many hospitals provide car seat safety checks as part of their prenatal and postnatal services. They may also offer classes on proper car seat installation and usage.
- Fire Departments: Fire departments often have certified technicians who can assist with car seat installation and provide safety inspections.
- Community Centers: Local community centers and parenting groups frequently host workshops and events focused on car seat safety, providing education and hands-on assistance.
Manufacturer Support
Contacting Car Seat Manufacturers for Assistance
Car seat manufacturers are an essential resource for specific questions and concerns about their products. They can provide:
- Customer Service Hotlines: Many manufacturers offer customer service hotlines where parents can ask questions about car seat installation, maintenance, and safety.
- Instructional Materials: Manufacturers’ websites typically offer downloadable instruction manuals, installation videos, and safety tips tailored to their specific products.
- Recall Information: By registering your car seat with the manufacturer, you will receive updates about any recalls or safety notices, ensuring that your car seat remains safe and effective.
By utilizing these resources, parents and guardians in Florida can ensure they are well-informed and equipped to provide the best possible protection for their children. Car seat inspection stations, online resources, community programs, and manufacturer support all play crucial roles in enhancing child passenger safety.
Understanding and adhering to Florida car seat laws is essential for the safety of your child passengers. Florida’s regulations require children aged five and under to be secured in a federally approved child restraint system, with specific guidelines based on age, weight, and height. Proper installation and usage of rear-facing, forward-facing, and booster seats, along with correct seat belt use, are critical. Additionally, being aware of common mistakes, such as incorrect placement and harness positioning, and following manufacturer guidelines can significantly enhance safety.
Child passenger safety is an ongoing process that requires regular attention and updates. Continually reviewing and adhering to the latest safety guidelines and regulations, including booster seat age Florida requirements, is crucial. Regularly inspect your car seat for wear and tear, ensure it is properly installed and fits your child correctly, and replace it as needed, especially after accidents or upon reaching its expiration date. Utilize resources like car seat inspection stations, online guides, and community programs to stay informed and ensure compliance with current safety standards.
Ensuring your child’s safety while traveling is a paramount responsibility, but it is manageable with the right knowledge and resources. By understanding Florida’s car seat laws and best practices, you can provide the highest level of protection for your children. Remember, the correct use of car seats and seat belts can dramatically reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident. Stay vigilant, keep informed, and do not hesitate to seek help from certified technicians or trusted resources to ensure your car seat is installed and used correctly. Your diligence and commitment to following these guidelines will significantly contribute to the safety and well-being of your children on the road.
Age -Championing Transparency and National Security: The Inspiring Journey of PSVF Fellow Ana Bower and Anna Bower’s Age
Consent for Routine Medical Care A Comprehensive Guide, Including What is the Age of Consent in Virginia
Navigating the Complexities of Consent Washington Age of Consent, Sexting, and Legal Implications
Understanding Sexual Consent Laws and the Virginia Legal Age of Consent in the Commonwealth
Travis bagent’s age “The Beast” The Unstoppable Force in Arm-Wrestling’s History and His Age
A Comprehensive Look at the Model’s Career, Impact, and Nikki Howard Age
Essential Laws Every Tourist Should Know, Including the Legal Drinking Age in Cancun, Mexico




 | Sitemap | Mail
| Sitemap | Mail